Network ports are given by the TCP or UDP conventions at the Vehicle layer. They are utilized by conventions in the upper layers of the OSI model. Port numbers are utilized to figure out what convention approaching traffic ought to be coordinated to. Ports permit a solitary host with a solitary IP address to run network administrations. Each port number recognizes a particular help, and each host can have 65535 ports for every IP address. Port use is managed by the Web Enterprise for Doling out Names and Numbers (ICANN). By ICANN there are three classifications for ports:
From 0 to 1023 – notable ports alloted to normal conventions and administrations, From 1024 to 49151 – enrolled ports doled out by ICANN to a particular help. From 49152 to 65 535 – dynamic (private, high) ports range from 49,152 to 65,535. Can be utilized by any help on a specially appointed premise. Ports are relegated when a meeting is laid out, and delivered when the meeting closes.
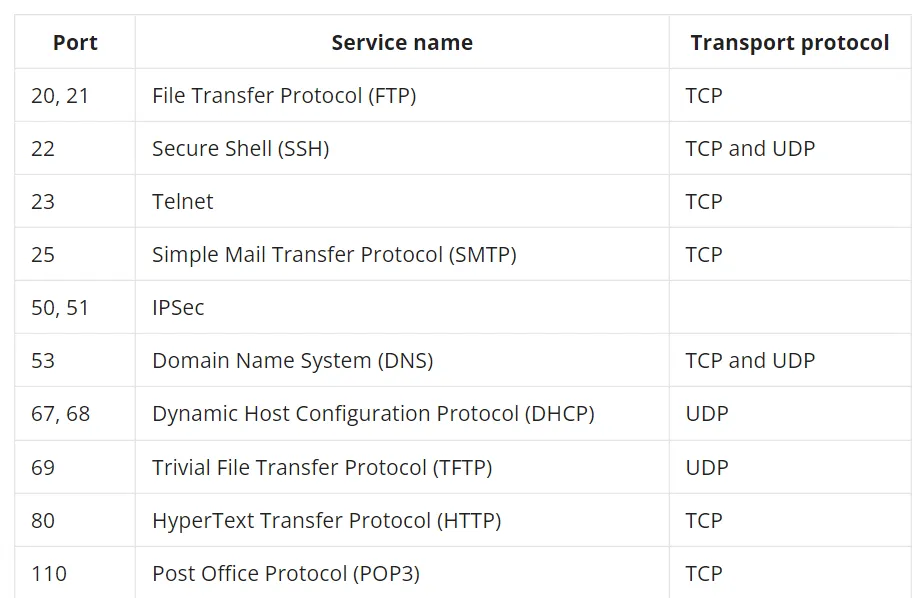
Well known ones are:
| Port | Service name | Transport protocol |
|---|---|---|
| 20, 21 | File Transfer Protocol (FTP) | TCP |
| 22 | Secure Shell (SSH) | TCP and UDP |
| 23 | Telnet | TCP |
| 25 | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) | TCP |
| 50, 51 | IPSec | |
| 53 | Domain Name System (DNS) | TCP and UDP |
| 67, 68 | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) | UDP |
| 69 | Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) | UDP |
| 80 | HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) | TCP |
| 110 | Post Office Protocol (POP3) | TCP |
| 119 | Network News Transport Protocol (NNTP) | TCP |
| 123 | Network Time Protocol (NTP) | UDP |
| 135-139 | NetBIOS | TCP and UDP |
| 143 | Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP4) | TCP and UDP |
| 161, 162 | Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) | TCP and UDP |
| 389 | Lightweight, Directory Access of Protocol | TCP & UDP |
| 443 | HTTP with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) | TCP & UDP |
| 989, 990 | FTP over SSL/TLS (implicit mode) | TCP |
| 3389 | Remote Desktop Protocol | TCP & UDP |
More About Common Ports:
Witin PC organizing, ports fill a comparable need. At the point when a PC framework tries to interface with another PC, the port fills in as a correspondence endpoint. It is additionally workable for various administrations running on a similar PC to uncover different ports and speak with each other utilizing these ports. In straightforward terms, on the off chance that a product application or administration needs to speak with others, it will uncover a port. Ports are related to positive 16-digit unsigned whole numbers, going from 0 to 65535. Different administrations utilize this port number to speak with the help or application. Port numbers are partitioned into three territories: notable ports, enlisted ports, and dynamic or confidential ports.
Notable ports (otherwise called framework ports) are numbered from 0 through 1023. For instance, to associate with the host example.com through SSH, I would utilize this order:
ssh [email protected] – v
In this model, – v represents verbose, and you ought to see yield like this:
debug1: Interfacing with example.com [<IP Addr>] port 22
As displayed, SSH is attempting to interface with example.com utilizing port number 22. You might utilize the – p choice to determine another port number; if not, SSH will default to 22.
What is a port?
Ports are programming based and oversaw by a PC’s working framework. Each port is related with a particular interaction or administration. Ports permit PCs to separate between various types of traffic: messages go to an unexpected port in comparison to pages, for example, despite the fact that both arrive at a PC over a similar Web association without any problem.
What is a port number?
Most ports are held for specific conventions — for instance, all Hypertext Move Convention (HTTP) messages go to port 80. While IP tends to empower messages to go to and from explicit gadgets, port numbers permit focusing of explicit administrations or applications inside those gadgets.